Spring Boot has made building a web application way easier. It has also added a lot of other critical libraries that help enterprise applications in different ways. With enterprise applications moving to the cloud, Spring Boot has made it easier to deploy spring applications in the cloud with continuous integration. In this post, I will show how we can use a spring micrometer library to gather analytics related to your code.
As a result, these analytics can be transferred to different vendor databases for creating metrics-based dashboards. I showed how to use spring-boot-actuator to collect some metrics data.
As Spring defines Micrometer is a dimensional-first metrics collection facade. In simple words, it is similar to SLF4J, except for metrics.
Configure Micrometer for microservice
Firstly to use a micrometer, I have created a simple microservice with REST APIs and it is built using Spring Boot 2. Most importantly Spring Boot has added backward compatibility for Spring 1.x.
You can configure Micrometer in your Spring Boot 2.X based Microservice by adding the following dependency in your build file
runtime('io.micrometer:micrometer-registry-prometheus:1.0.4')
Adding Metrics
We will discuss different metrics that we can add through the micrometer. Dimensions and names identify a meter. You can use Meter for different types of metrics.
Counter
Counters are a cumulative metric. These are mostly used to count the number of requests, number of errors, number of tasks completed.
Gauges
A gauge represents a single value that can go up and down. The gauge measures memory usage.
Timers
Timers measure the rate at which we call a particular code or method. Subsequently we can also find out latencies when the execution of code is complete.
We talked about different metrics and how we can configure micrometers. Now we will show how to use this library to configure against a monitoring system. Spring micrometer supports the number of the monitoring system. In this post, I will be showing how to use against Prometheus monitoring system.
What is Prometheus?
Prometheus is an in-memory dimensional time-series database with a built-in UI, a custom query language, and math operations. To know more, you can visit here.
Meanwhile, we can add Prometheus in our microservice by adding the following dependency in the Gradle file
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator:2.0.3.RELEASE')
runtime('io.micrometer:micrometer-registry-prometheus:1.0.4')
For example, to understand where Prometheus lies in whole architecture, look at the below
Spring Boot microservice -> Spring Micrometer -> Prometheus
Once the above dependencies are added, Spring boot will automatically configure PrometheusMeterRegistry and CollectorRegistry to collect and export metrics data in a suitable format that Prometheus can scrape.
To enable Prometheus endpoints
Similarly, you enable Prometheus and actuator endpoints. Add following properties in application.properties file
management.security.enabled = false management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=health,info,prometheus
Now if we run to start our webserver to see how these endpoints look, we can verify by going to endpoints http://localhost:8080/actuator/info , http://localhost:8080/actuator/health and http://localhost:8080/actuator/prometheus . Prometheus endpoint looks like below :
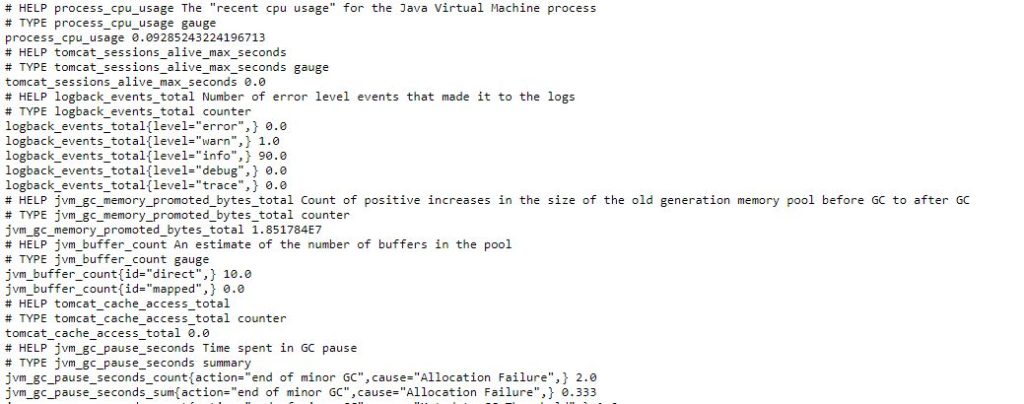
Prometheus
Conclusion
In this post, we showed how to use Spring Micrometer to capture metrics data and configure with Prometheus. In the next post, I will show how to display this data in the human-readable format in nice UI using Prometheus.
References
- Production-Ready Metrics – Metrics
- Spring Micrometer – Spring Micrometer